LeetCode-46 全排列
题目
结果
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new LinkedList<>();
if (nums.length == 0) {
return ans;
}
List<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
boolean[] used = new boolean[nums.length];
dfs(nums, path, 0, used, ans);
return ans;
}
private void dfs(int[] nums, List<Integer> path, int depth, boolean[] used, List<List<Integer>> ans) {
if (depth == nums.length) {
ans.add(new LinkedList<>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (!used[i]) {
path.add(nums[i]);
used[i] = true;
dfs(nums, path, depth + 1, used, ans);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
used[i] = false;
}
}
}
}
|
算法
深度优先遍历
深度优先遍历不是对树的算法吗?不,心中有树就可以。
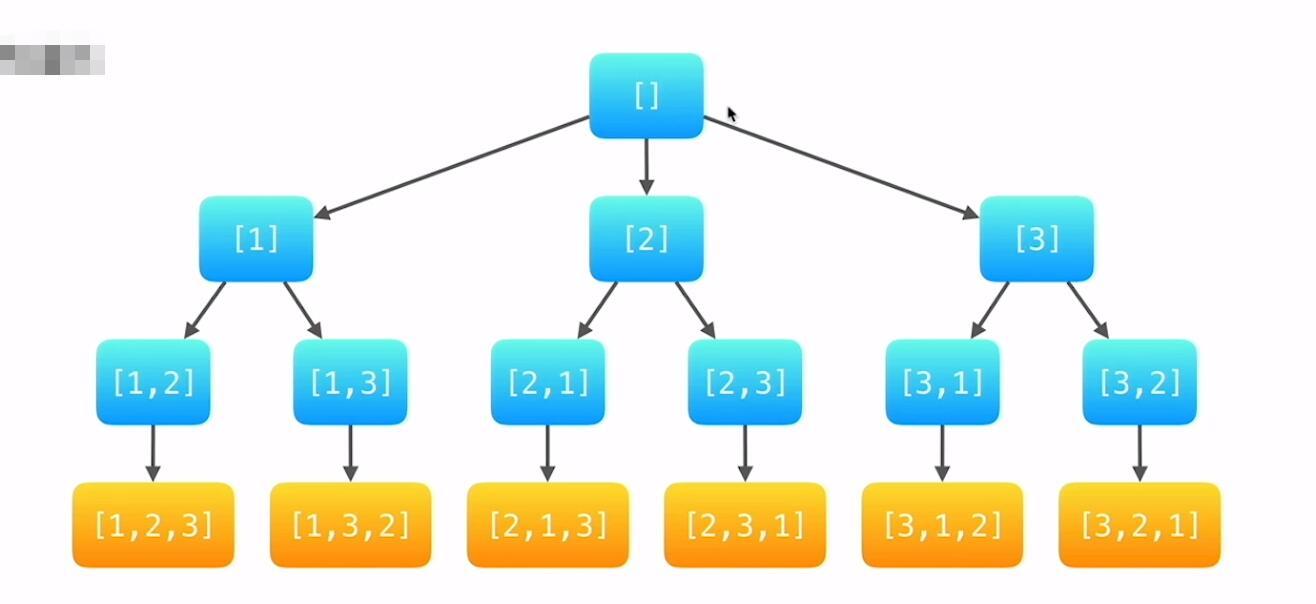
和一般的深度优先遍历不同的是,这个DFS的作用对象不是树,但我们可以想象出一颗树,这个树的结构很简单,它罗列出了所有可能的情况。
我们递归地深度遍历这棵不存在的树,用path记录遍历过节点的元素,用used数组记录已经遍历过的节点,遍历到叶子节点时(nums.length == depth)就停止递归,并回溯(清除当前状态:used,path,depth)。




